Dinosaur Knowledge Tips Stegosaurus
Release time:2017/10/21 10:09:00
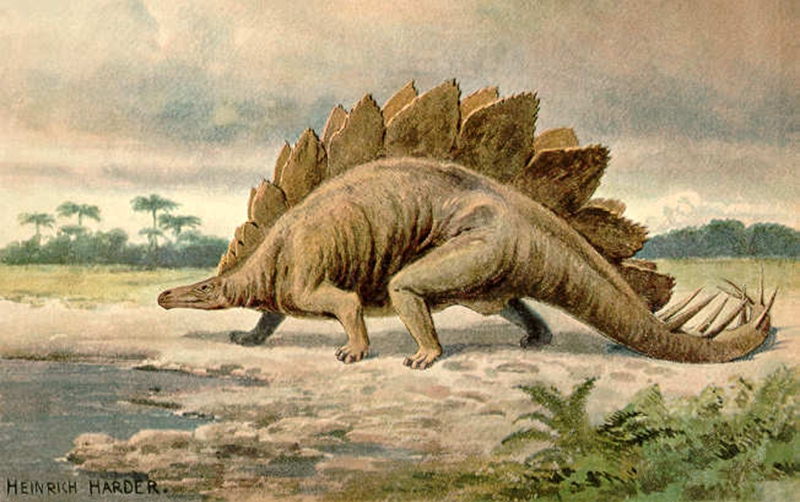
Stegosaurus () is a genus of thyreophoran dinosaur. Fossils of this genus date to the Late Jurassic period, where they are found in Kimmeridgian to early Tithonian aged strata, between 155 and 150 million years ago, in the western United States and Portugal. Several species have been classified in the upper Morrison Formation of the western U.S, though only three are universally recognized; S. stenops, S. ungulatus and S. sulcatus. The remains of over 80 individual animals of this genus have been found. Stegosaurus would have lived alongside dinosaurs such as Apatosaurus, Diplodocus, Brachiosaurus, Allosaurus, and Ceratosaurus; the latter two may have been predators of it.
These were large, heavily built, herbivorous quadrupeds with rounded backs, short fore limbs, long hind limbs, and tails held high in the air. Due to their distinctive combination of broad, upright plates and tail tipped with spikes, Stegosaurus is one of the most recognizable kinds of dinosaur. The function of this array of plates and spikes has been the subject of much speculation among scientists. Today, it is generally agreed that their spikes were most likely used for defense against predators, while their plates may have been used primarily for display, and secondarily for thermoregulatory functions. Stegosaurus had a relatively low brain-to-body mass ratio. It had a short neck and a small head, meaning it most likely ate low-lying bushes and shrubs. One species, Stegosaurus ungulatus, is the largest known of all the stegosaurians (bigger than related dinosaurs such as Kentrosaurus and Huayangosaurus).
Stegosaurus remains were first identified during the "Bone Wars" by Othniel Charles Marsh. The first known skeletons were fragmentary and the bones were scattered, and it would be many years before the true appearance of these animals, including their posture and plate arrangement, became well understood. The name Stegosaurus means "roof lizard" or "covered lizard", in reference to its bony plates. Despite its popularity in books and film, mounted skeletons of Stegosaurus did not become a staple of major natural history museums until the mid-20th century, and many museums have had to assemble composite displays from several different specimens due to a lack of complete skeletons. As the archetypal thyreophoran, Stegosaurus is one of the best-known dinosaurs, and has been featured in film, postal stamps, and many other types of media.
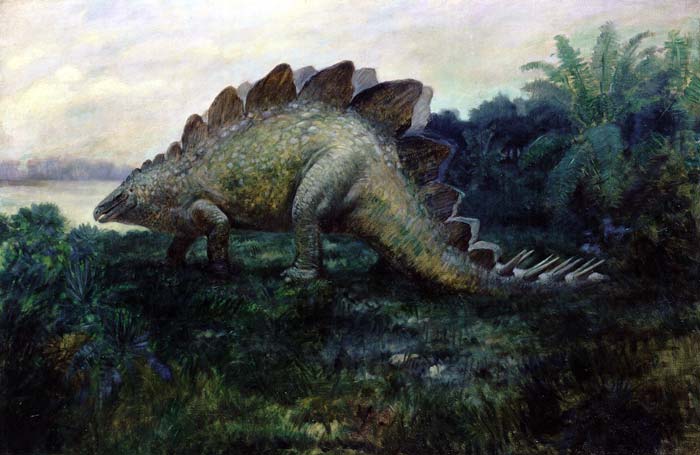

The quadrupedal Stegosaurus is one of the most easily identifiable dinosaur genera, due to the distinctive double row of kite-shaped plates rising vertically along the rounded back and the two pairs of long spikes extending horizontally near the end of the tail. Although large individuals could grow up to 9 m (29.5 ft) in length and 5.3–7 tonnes (12,000–15,000 lb) in weight, the various species of Stegosaurus were dwarfed by contemporaries, the giant sauropods. Some form of armor appears to have been necessary, as Stegosaurus species coexisted with large predatory theropod dinosaurs, such as Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus.
Most of the information known about Stegosaurus comes from the remains of mature animals; more recently, though, juvenile remains of Stegosaurus have been found. One subadult specimen, discovered in 1994 in Wyoming, is 4.6 m (15.1 ft) long and 2 m (6.6 ft) high, and is estimated to have weighed 2.4 metric tons (2.6 short tons) while alive. It is on display in the University of Wyoming Geological Museum.

from
Wikipedia